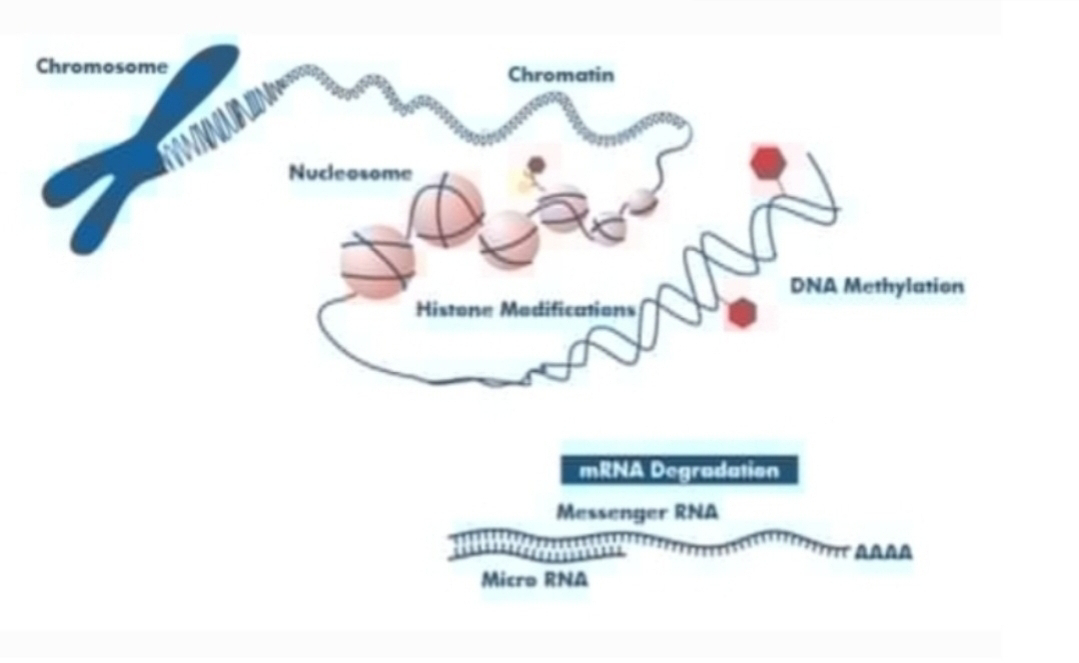
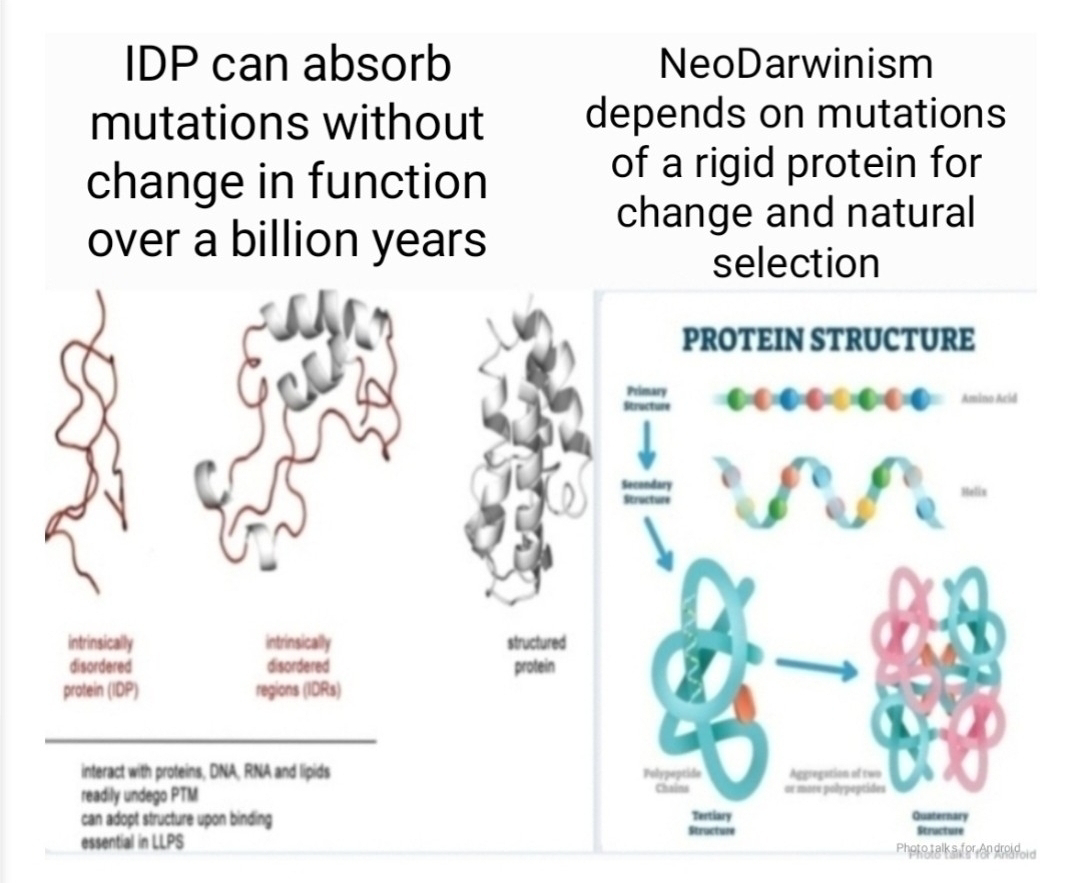
The Architecture of Life: How Hierarchical Evolutionary-Developmental Theory and Epigenetics Reframe Darwin

A new perspective is challenging the long-held tenets of neo-Darwinism, offering a more integrated and multi-layered understanding of the evolutionary process. This emerging framework, known as Hierarchical Evolutionary-Developmental Theory (H-Evo-Devo), repositions the organism and its developmental processes at the heart of evolutionary change. By incorporating principles of hierarchy and the crucial role of epigenetics, this theory presents a significant challenge to the gene-centric view that has dominated evolutionary thought for nearly a century, proposing a more holistic and dynamic picture of how life diversifies and innovates. At its core, H-Evo-Devo theory posits that evolution operates on multiple, nested levels of biological organization, from the familiar microevolutionary changes within populations to the grander macroevolutionary and even "mega-evolutionary" patterns that shape the entire tree of life. This contrasts sharply with the traditional neo...